What is Bladder Cancer?
Bladder cancer is a type of cancer that starts in the cells of the bladder, which is a hollow organ responsible for storing urine.
What Causes Bladder Cancer?
The most significant risk factor is smoking, which accounts for nearly half of all bladder cancer cases. Exposure to certain chemicals, such as those found in industrial workplaces, can also contribute to the development of bladder cancer. People with a family history of bladder cancer have a higher likelihood of being diagnosed with the disease. Chronic bladder inflammation and certain bladder birth defects are also known to increase the risk. Certain medications, such as cyclophosphamide, used in the treatment of other cancers, may raise the chances of developing bladder cancer.
Types of Bladder Cancer:
Urothelial Carcinoma (Transitional Cell Carcinoma)
This is the most common type of bladder cancer, accounting for about 90% of all cases. It develops in the urothelial cells, which are the cells lining the inside of the bladder.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma
This type of bladder cancer starts in the thin, flat cells that are found in the bladder after long-term infections or irritation. It accounts for about 1-2% of all bladder cancers.
Adenocarcinoma
A rare type of bladder cancer starting in the cells that make and release mucus and other fluids. Adenocarcinoma accounts for about 1% of all bladder cancers.
Small Cell Carcinoma
A rare and aggressive type of bladder cancer that develops in the neuroendocrine cells of the bladder. It accounts for less than 1% of all bladder cancers.
Lymphoma
A rare bladder cancer that arises in the bladder’s immune system cells and accounts for less than 1% of all bladder cancers.
Sarcoma
Another rare type of bladder cancer that originates in the bladder’s connective tissues. It accounts for less than 1% of all bladder cancers.
What are the common symptoms of bladder cancer?
The most frequent symptom is blood in the urine. Other common symptoms include:
- Frequent urination
- Persistent urge to urinate
- Pain or burning during urination
- Pelvic or back pain
How to Prevent Bladder Cancer
Preventing bladder cancer involves adopting certain lifestyle habits and making informed choices. Avoiding smoking, or quitting smoking altogether is crucial as it is the leading cause of bladder cancer. Maintaining a healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can also reduce the risk. Staying hydrated by drinking plenty of water and limiting the intake of harmful chemicals and substances found in certain workplaces is advisable. Regular exercise and maintaining a healthy weight can also contribute to reducing the risk of bladder cancer. Being mindful of exposure to chemicals and toxins and taking necessary precautions can also be a preventive measure. It is important to undergo regular check-ups and screenings, especially if you have a family history of bladder cancer or other risk factors.
How Do We Diagnose Bladder Cancer
Bladder cancer is diagnosed through various methods that help in determining the presence, grade, and stage of the cancer. Some of the common diagnostic techniques include cystoscopy, fish urine test, and exosome analysis.
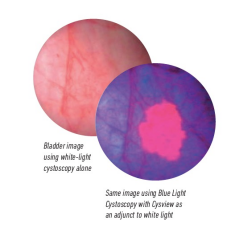
Cystoscopy is a procedure that allows the doctor to examine the inside of the bladder and urethra. It is performed using a thin, flexible tube called a cystoscope that is inserted through the urethra. There are different types of cystoscopy, one of which is Blue Light cystoscopy. Blue Light cystoscopy uses a special dye that makes cancer cells glow under blue light, allowing doctors to easily identify and remove any abnormal tissue. This technique enhances the accuracy of detecting bladder cancer, especially the more aggressive forms.
Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization (FISH) urine test is a non-invasive diagnostic tool that detects genetic abnormalities associated with bladder cancer. It involves analyzing a urine sample for abnormalities in DNA content, and it can identify genetic mutations that are commonly found in bladder cancer cells. FISH urine tests can help determine the presence of bladder cancer and its recurrence, as well as evaluate the risk of its progression to a higher grade.
Exosome analysis is a cutting-edge diagnostic technique that analyzes exosomes, small vesicles released by cancer cells, to evaluate the risk of high-grade bladder cancer. Exosomes carry molecular information about the cancer and analyzing them can provide insights into the aggressiveness and progression of the disease. This non-invasive test assists in identifying patients who are at higher risk of developing high-grade bladder cancer, enabling targeted and personalized treatment approaches.
Who is At Risk for Developing Bladder cancer?
Certain factors can contribute to an individual’s likelihood of developing bladder cancer. The most significant risk factor is smoking, which is responsible for approximately half of all bladder cancer cases. Exposure to certain chemicals and substances, such as arsenic, aromatic amines, and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, can also increase the risk of bladder cancer. Having a family history of bladder cancer, chronic bladder infections, long-term catheter use, previous radiation therapy, or a history of bladder birth defects or stones can also elevate the risk. Age and gender also play a role, as men and older individuals face a higher risk. Caucasians also have a higher incidence of bladder cancer compared to other ethnic groups.
Can bladder cancer be prevented?
While it is not possible to prevent bladder cancer entirely, certain measures can be taken to help reduce the risk. The most important step is to quit smoking or avoid starting in the first place, as smoking is the leading cause of bladder cancer. Limiting exposure to harmful chemicals and substances in the workplace or environment can also reduce the risk. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle with a balanced diet, regular exercise, and staying properly hydrated may also contribute to reducing the risk of bladder cancer.
If you are experiencing symptoms such as blood in your urine, frequent urination, or pelvic pain, it is crucial that you get evaluated by a healthcare professional. Our team of medical experts are here to provide the expertise and care you need. Don’t wait, call NY Urology today to ensure early detection and better outcomes.
