What Are Kidney Stones?
Kidney stones, also known as renal calculi, are hard deposits that form in the kidneys. They can range in size from a tiny grain of sand to a larger stone that can be several centimeters in diameter. Kidney stones can be made up of various substances, such as calcium, uric acid, and cystine. When these substances accumulate and crystallize in the urine, they can form solid masses, causing discomfort and sometimes intense pain.
What Causes Kidney Stones?

Diet
Certain foods like spinach, peanuts, and chocolate are high in oxalates, which can bind with calcium and form kidney stones.

Hydration
Not drinking enough fluids allows minerals to concentrate in your urine, increasing the risk of stones.
Types of Kidney Stones


Uric Acid Stones may appear smooth or have a rough texture. These stones may range in size from very small, resembling grains of sand, to larger, more noticeable stones. In some cases, they can grow to be large enough to fill up an entire kidney. Uric acid stones may also have irregular shapes, sometimes resembling jagged crystals. Some of these stones may be hard on the outside, but softer on the inside as they consist of different types of uric acid and calcium oxalate monohydrate. These stones are primarily composed of uric acid, a waste product generated when the body breaks down purines, a substance found in certain foods and drinks. Uric acid stones can cause significant pain and discomfort, as they can block the flow of urine and lead to symptoms like intense back or abdominal pain, blood in urine, and frequent urination. Factors such as a high intake of protein, certain medical conditions like gout, and insufficient fluid intake can increase the risk of developing uric acid kidney stones. Treatment usually involves pain management, increased hydration, dietary changes to reduce purine consumption, and sometimes medication to help dissolve or prevent the formation of these stones.

Cystine kidney stones are a type of kidney stone that is made up of cystine, an amino acid. These stones form when there is an excess amount of cystine in the urine, leading to the formation of crystals. Cystine stones are relatively rare, accounting for about 1-2% of all kidney stones. They tend to be larger and more difficult to pass compared to other types of kidney stones. Cystinuria, an inherited condition, is the main cause of cystine stones. This condition affects the reabsorption of cystine by the kidneys, leading to its accumulation and eventual formation of stones. Treatment options for cystine stones include drinking plenty of fluids to help flush out the stones, medications to reduce cystine levels in the urine, and occasionally surgical intervention to remove the stones.

Struvite stones, also known as infection stones, are a type of kidney stone that is composed of magnesium ammonium phosphate. These stones typically form in individuals with urinary tract infections caused by certain bacteria. The bacteria produce an enzyme called urease, which raises the pH of the urine and creates an environment conducive to the formation of struvite stones. Struvite stones can grow quickly and can become quite large, often filling the entire renal pelvis and even extending into the ureter. They can cause a variety of symptoms, including sudden and severe pain, blood in the urine, and frequent urination. Treatment for struvite stones involves addressing the underlying infection and removing the stones through procedures such as lithotripsy or surgical intervention. Preventive measures such as antibiotic therapy and maintaining a healthy urinary tract can help prevent the recurrence of struvite stones.
What Are the Symptoms
of Kidney Stones?
- Severe pain on the back or side
- Severe pain on the back or side Blood in the urine (hematuria)
- Frequent urination
- Pain or burning sensation when urinating
- Nausea and vomiting
- Cloudy or foul-smelling urine
- Pink, red, or brown urine
- Persistent need to urinate
How Are Kidney Stones Diagnosed?
- Medical History & Exam: We'll discuss your symptoms and gently examine your back and abdomen to pinpoint any tenderness.
- Imaging Tests: X-rays, CT scans, or ultrasounds get a clear picture of the stone's location and size.
- Lab Tests: A urine analysis reveals any mineral or chemical imbalances contributing to the stone formation.
How To Get Rid of Kidney Stones?
Getting rid of kidney stones can be a challenging process, but with the right approach, it is possible to alleviate the discomfort they bring. One crucial aspect is maintaining a healthy diet. It is recommended to limit the consumption of red meat and foods high in oxalate, such as spinach, as they may contribute to stone formation. Additionally, staying well-hydrated is essential to prevent the build-up of minerals in the kidneys. Drinking plenty of water throughout the day helps to flush out toxins and keep urine diluted. Furthermore, it is vital to monitor any changes in urinary habits, such as the presence of blood or pain while urinating. Consulting a healthcare professional and regularly monitoring these symptoms can help in the prevention and timely treatment of kidney stones.
What Are The Treatment Options for Kidney Stones?
The treatment of kidney stones depends on various factors, including the size, location, and composition of the stones, as well as the severity of symptoms. Smaller stones often pass through the urinary tract on their own with the help of pain medication and increased fluid intake. For larger stones that cannot easily pass, medical intervention may be necessary. At Modern Urology, we’re dedicated to providing the latest and most effective treatments for kidney stones!
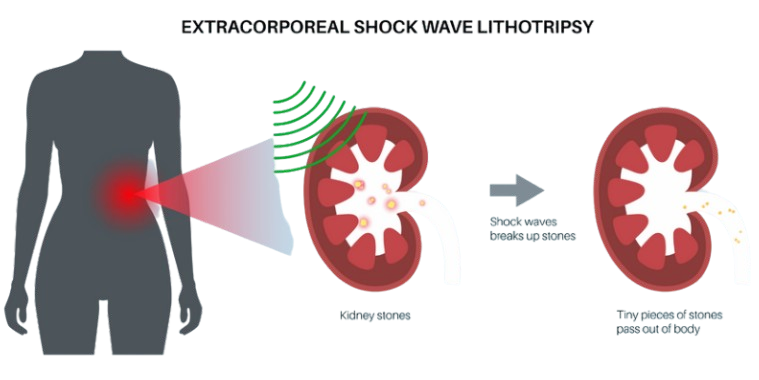
If you or someone you know is suffering from kidney stones, you don’t have to endure the pain alone. Our team at NY Urology is here to help. Don’t let kidney stones disrupt your life any longer. Call us today and schedule an appointment!
